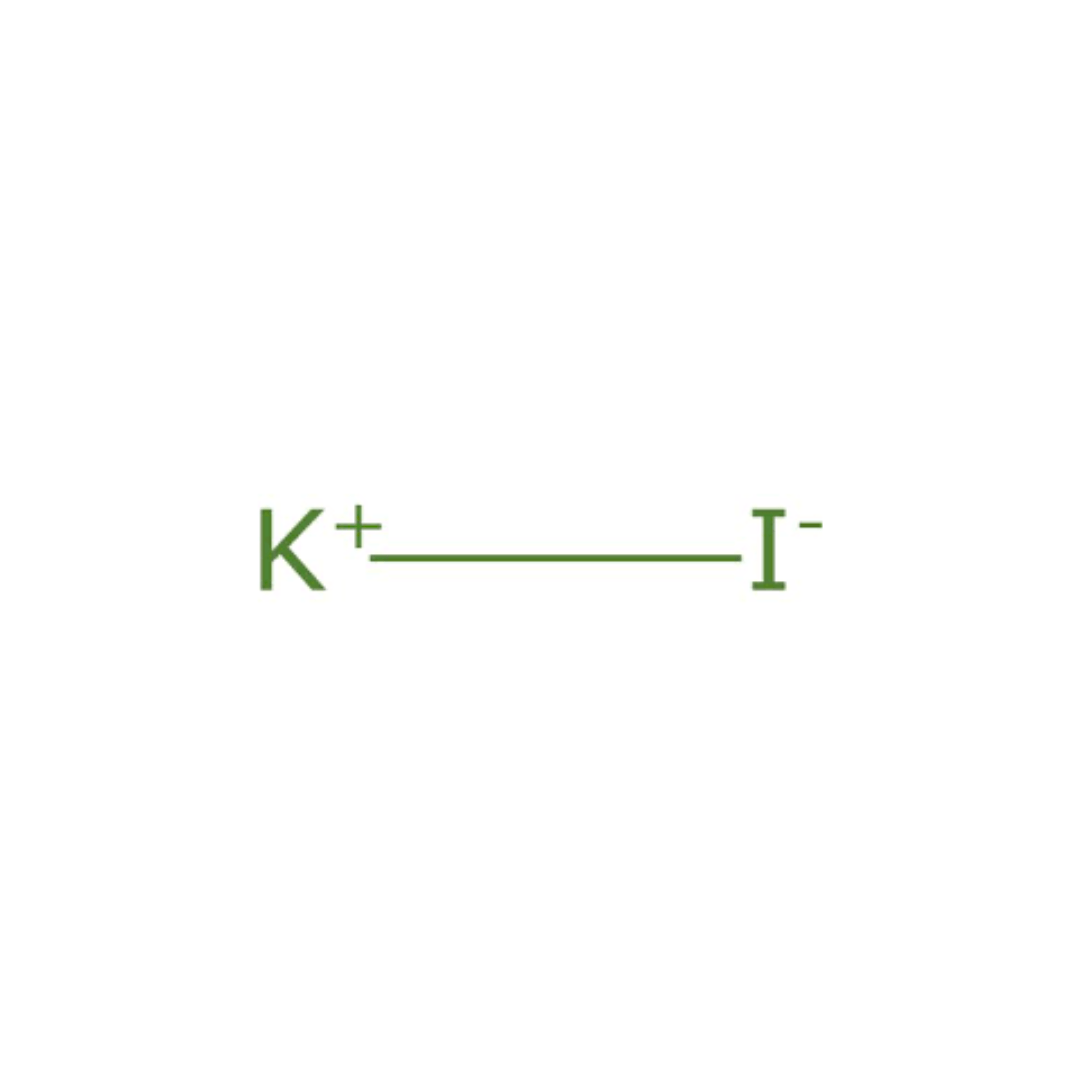General Information
Potassium iodide is a chemical compound composed of potassium and iodine ions. It is widely used in various applications, including pharmaceuticals, dietary supplements, and radiation emergency preparedness. Potassium iodide serves as a source of iodine, an essential micronutrient crucial for thyroid function, hormone synthesis, and overall health. Its role in medical treatments, iodine supplementation, and radiation protection underscores its significance in healthcare and public safety.
Renowned for its stability and bioavailability, potassium iodide is a preferred choice for iodine supplementation and thyroid protection in emergency situations. Its significance extends beyond its chemical composition, impacting human health and well-being through various applications.
Specifications
Potassium iodide typically presents as white crystalline powder or granules. It is highly soluble in water and exhibits a salty taste. The compound’s purity and particle size may vary depending on its intended use, ranging from pharmaceutical-grade to industrial-grade formulations. Potassium iodide conforms to regulatory standards for purity and safety, ensuring its suitability for various applications.
Properties
- White crystalline powder or granules
- Highly soluble in water
- Salty taste
- Stable and bioavailable source of iodine
- Meets pharmaceutical and industrial standards
Primary Functions
- Source of iodine for thyroid function and hormone synthesis
- Radiation protective agent in emergency situations
Applications
Potassium iodide is utilized in pharmaceutical formulations for iodine supplementation, particularly in the treatment of iodine deficiency disorders and thyroid conditions. Its bioavailability and stability make it suitable for oral administration in various dosage forms, including tablets, solutions, and topical preparations.
Potassium iodide is recommended for use as a thyroid-blocking agent in the event of nuclear accidents or incidents involving radioactive iodine exposure. Its ability to saturate the thyroid